The meat and poulty processing industry is a vital element of America’s food infrastructure and President Trump recently signed an executive order to keep it operating through the COVID-19 crisis. Despite the risk to the 500,000 people employed in the industry, it gives the Secretary of Agriculture the power to invoke the Defense Production Act in order to keep processing plants up and running.
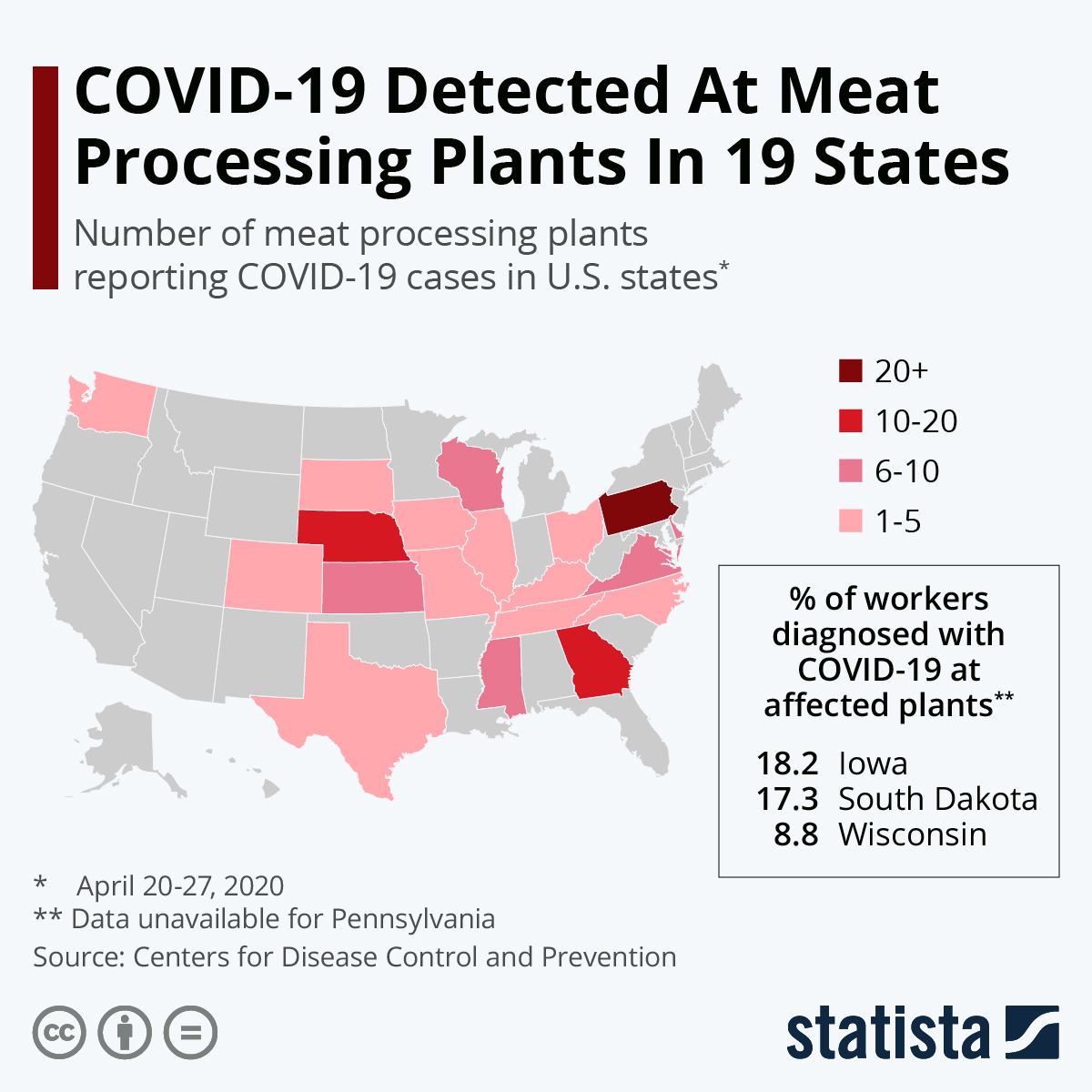
The industry is particularly vulnerable to an infectious respiratory disease such as COVID-19 as the bulk of its work is conducted in close quarters and reports have been emerging about serious outbreaks in meat processing plants over the past few weeks. A new CDC report has now found that COVID-19 was detected at 115 meat processing plants across 19 U.S. states between April 20 and 27, 2020.
130,000 people are working in those affected plants and 4,913 of them (3 percent) tested positive for the coronavirus during the above period. Unfortunately, 20 of them have died. Pennsylvania has the highest number of plants with confirmed cases (22) with Georgia (14) and Nebraska (12) following.
Even though only two processing plants have reported infections in Iowa, the state has the highest rate of COVID-19 at its affected facilities at 18.2 percent. South Dakota’s affected plants have an infection rate of 17.3 percent while Wisconsin hd the third highest figure at 8.8 percent. While Pennsylvania had the most affected locations, data regarding its infection rate was not available.
 You will find more infographics at Statista
You will find more infographics at Statista
Read more about: Coronavirus, COVID-19, food, Pandemics




